Hundreds of groups call for permanent telehealth benefits
More than 450 organizations, including AARP, urged Congress to make Medicare's expanded telehealth coverage permanent. Many groups joined a letter from the Alliance for Connected Care that asked Congress to provide a long-term telehealth fix for Medicare “to ensure stability and provide clarity for patients, providers and the health care system as a whole.”
The current “cycle of temporary fixes has resulted in patients and providers facing continued disruptions in care,” said the alliance, a coalition of health care and technology interests. Caregivers strapped for time to transport their loved ones have benefited from the convenience.
“It’s probably the only good thing that came out of COVID, frankly, in terms of improving access, because it’s been such a resounding success,” Nicholas Widmyer, director of federal affairs for the National Association of Community Health Centers based in Bethesda, Maryland, said last year. An end to these services “would be a step backwards for a lot of our patients’ ability to access primary care.”
Organizations including the alliance and the ATA, with nearly 500 industry members total, are pushing to continue the expanded telehealth options. Several bipartisan bills have been introduced that would continue the COVID-19 Medicare telehealth provisions or make them permanent. They include:
- A lasting solution. The Creating Opportunities Now for Necessary and Effective Care Technologies (CONNECT) for Health Act of 2025, H.R. 4206 and S. 1261, would erase the end date for the expanded telehealth provisions. Sen. Brian Schatz (D-Hawai‘i) reintroduced S. 1261 in April 2025, while Reps. Mike Thompson (D-Calif.) and David Schweikert (R-Ariz.) filed H.R. 4206 in June 2025. AARP has endorsed these companion bills.
- An extension. The Telehealth Modernization Act, H.R. 5081, was introduced in September 2025 by Reps. Buddy Carter (R-Ga.) and Debbie Dingell (D-Mich.). Sens. Tim Scott (R-S.C.) and Brian Schatz (D-Hawai‘i) also filed the Senate version, S. 2709, the same month. These bills would extend the Medicare telehealth flexibilities through Sept 30, 2027, less than what's in the budget deal signed Feb. 3.
All have been referred to committees without any action taken.
Pandemic changed perceptions of telemedicine
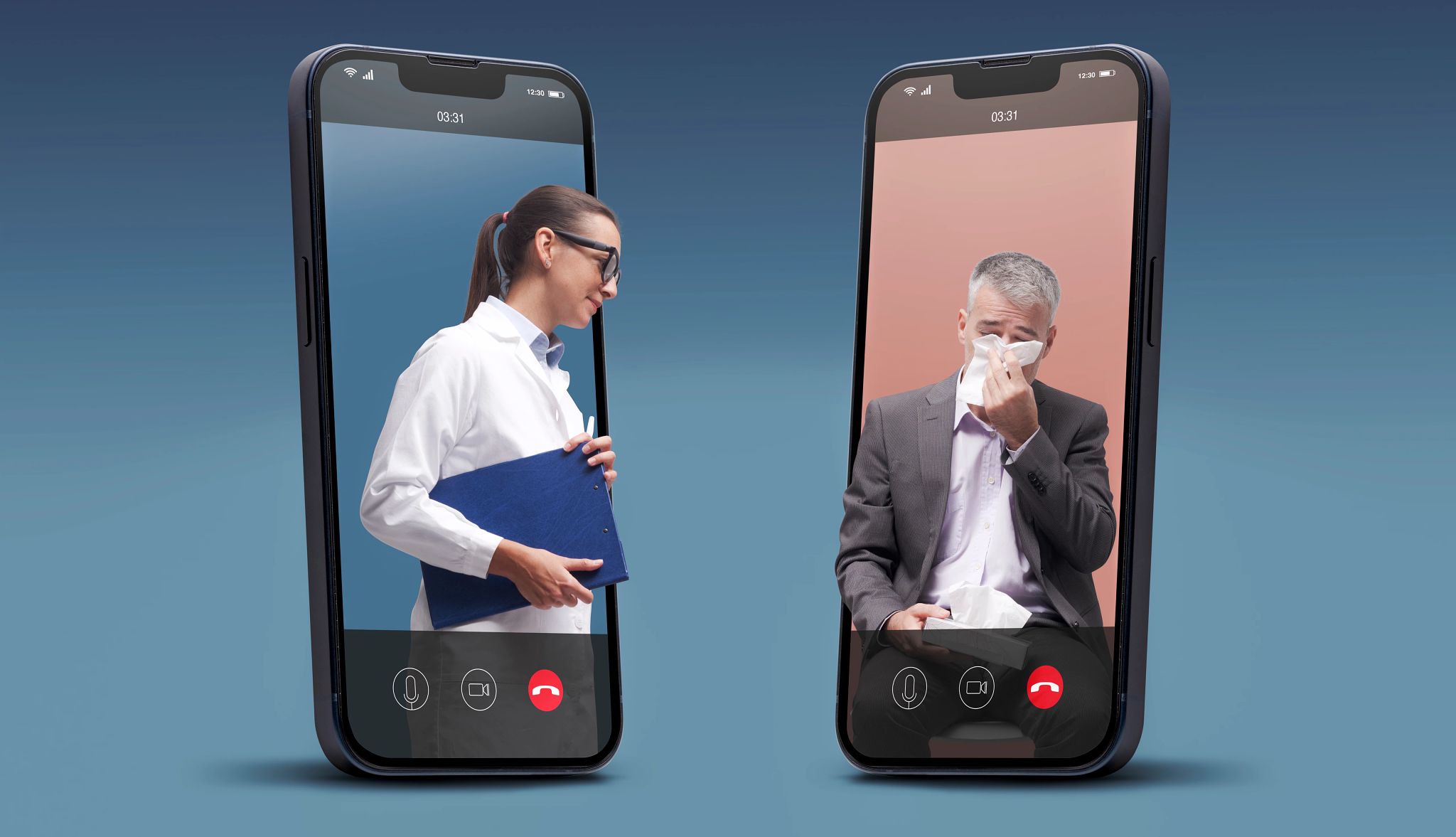
In the early part of the pandemic, nearly half of Medicare beneficiaries had at least one virtual medical visit between April and June 2020. And participation continued to be much higher than pre-pandemic levels, according to data from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
The original waiver was temporary, ending after the public health emergency was declared over on May 11, 2023. Congress subsequently folded extensions into various spending bills.
“Telehealth is important because it breaks down geographic barriers to care,” says Kyle Zebley, American Telemedicine Association chief executive officer. “It’s important to virtually every American.”
‘Telehealth is important because it breaks down geographic barriers to care. It’s important to virtually every American.’
— Kyle Zebley, American Telemedicine Association
Brown University research found that about 15 percent of all original Medicare beneficiaries had telehealth appointments in the first half of 2025, primarily to help monitor and treat chronic conditions.
Nearly three-quarters of adults 50 and older said they used telehealth services at least once in the past 12 months, according to a January 2024 AARP poll. Nine in 10 said they were somewhat or very satisfied with their experience; about half of those surveyed were on Medicare, the federal insurance program that helps pay health care costs for adults age 65 and older and some younger than 65 with disabling conditions.
Telehealth is most popular among people 65 and older with long-term disabilities, as well as those who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid, according to KFF, a nonpartisan nonprofit with offices in Washington that studies health care trends.







































































More From AARP
Medicare to Negotiate Prices on 15 More Drugs
The new lower prices will be released in fall 2026
Medicare Prescription Drug Prices Keep Climbing
The increases outpace inflation, AARP study shows
8 Changes Shaping Your Medicare Coverage in 2026
Medicare lowers drug costs, will cover some weight loss meds