AARP Hearing Center
Your BMI Calculator Results Guide: Underweight
Your BMI suggests you are underweight — explore these tips and resources


Photo Illustration: AARP; (Source: Getty Images)
You may be better able to fight disease and enjoy good health by achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Keep in mind that BMI has its limits in predicting your health risks based on weight, and recommendations differ based on a few variables. And as you age, your muscle tone plays a role. BMI can underestimate body fat in older people who have lost muscle mass.
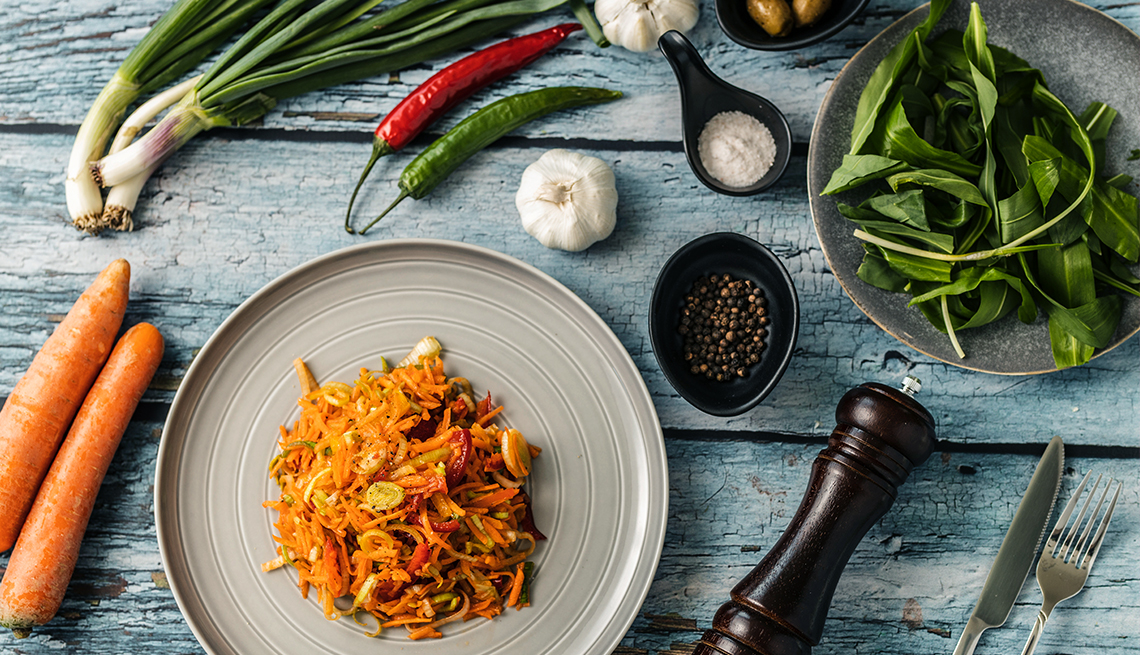
As you age, your body needs more protein for muscle and bone health. Healthy fats can help you gain weight without elevating your cholesterol levels.
Examples of lean proteins include white-fleshed fish, skinless white poultry meat, beans, lentils, tofu and Greek yogurt. Sources of healthy fats include nuts and seeds, salmon, avocado and olive oil. Sauté vegetables in olive oil instead of steaming or microwaving them. Add nuts or seeds to Greek yogurt, or enjoy a spoonful of peanut butter or other nut butter between meals.
Consider having nonalcoholic, calorie-rich beverages, such as a homemade smoothie or a nutritional drink like Boost or Ensure, between meals.
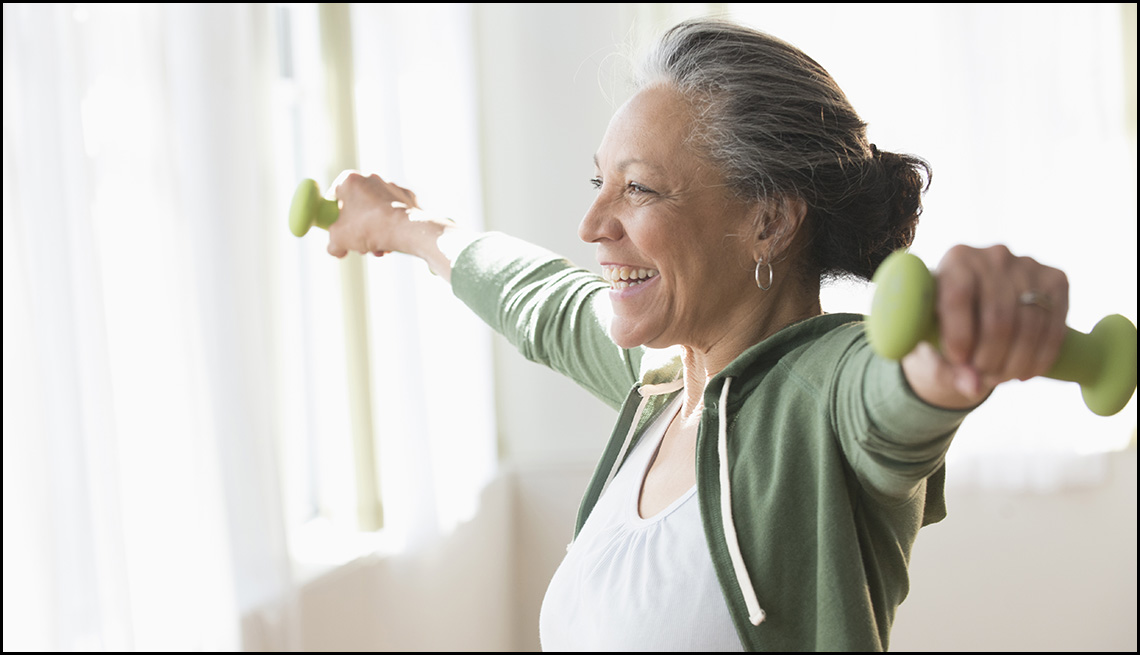
Muscle mass decreases as you age. To maintain muscle strength, incorporate a strength-training program that uses resistance bands or light weights. Stronger muscles not only help you perform everyday tasks more easily; they can also add weight to your frame and fight frailty.
Talk with your doctor about whether gaining weight could benefit your health. If so, work together and develop a strategy to gain weight in a safe, gradual manner.
Explore Health Articles
AARP Health Resources


AARP Membership — $15 for your first year when you sign up for Automatic Renewal
Get instant access to members-only products and hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP the Magazine.