AARP Hearing Center
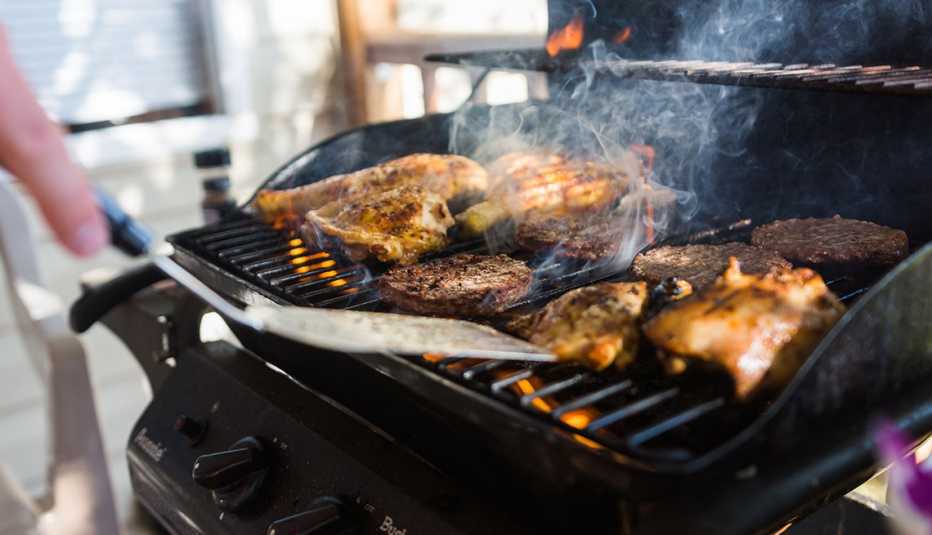


Whether it’s Labor Day or a random Tuesday, Americans are grilling more than ever. In fact, you can find a grill or smoker in 70 percent of American households, the highest percentage recorded since the Hearth, Patio & Barbecue Association (HPBA) began tracking consumer trends.
Grilling may be America’s favorite way to cook outdoors, but for most of us it’s not an everyday habit. That means even seasoned home chefs can slip up — and those mistakes can put your health at risk, especially for older adults.
“Food safety is important for everyone, but it’s extremely important for people who may be more vulnerable to severe food poisoning,” says Brian Katzowitz, who worked as a health communication specialist for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) when interviewed for this article. “Adults older than 65, because of weakened immune systems, may be more likely to get sick with a foodborne illness.”
To help weekend grill masters avoid exposing themselves and their dining companions to illnesses and other health risks, we asked for advice from Katzowitz and Robyn Goldberg, a registered dietitian, nutritionist and author of The Eating Disorder Trap.




































































More From AARP
Comparing Superfoods: What’s Better for You?
How to shop smart when buying plant-based burgers, fish, oil and more
How Much Do You Really Know About Food Poisoning?
Learn why older adults are at greater risk of foodborne illness and more in this challenging true-or-false quiz