AARP Hearing Center


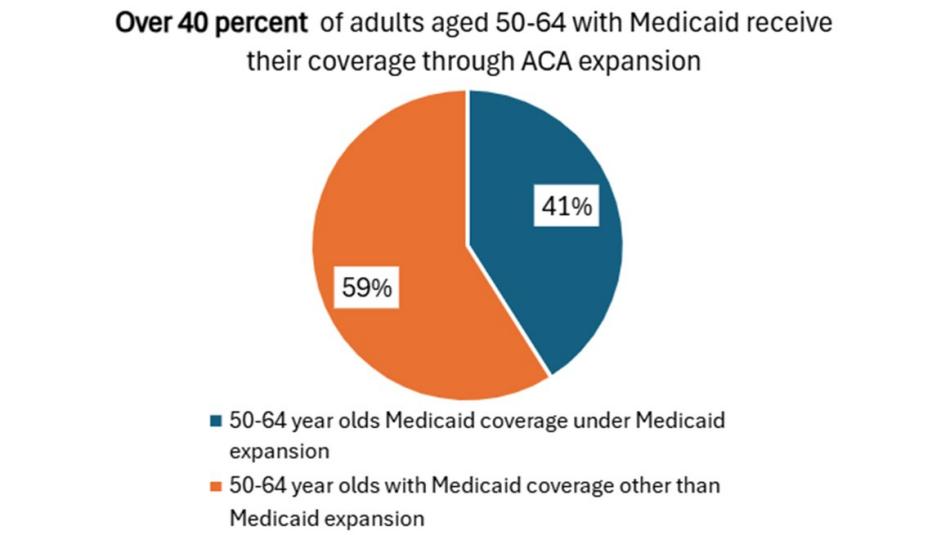
Forty-one states and the District of Columbia have expanded the Medicaid program to include many low-income adults who would not otherwise be eligible for the program. A significant number of older adults ages 50–64 depend on this coverage for critical services such as cancer screenings, primary care, and behavioral health care. Nearly 5 million older adults ages 50–64 are covered through the Medicaid expansion—representing approximately 41 percent of the entire Medicaid population in this age group.


Ongoing legislative efforts—most notably the recent “One Big Beautiful Bill”—have placed Medicaid coverage for older adults in jeopardy. With looming cuts to federal Medicaid funding, states will be forced to make tough budget decisions, potentially ending or reducing coverage for older adults who are insured through the Medicaid expansion. Many of the people affected would struggle to find other affordable health insurance and remain uninsured.
Using the data graphic
Click on a state to view data on its Medicaid expansion coverage, including the number and percentage of adults ages 50–64 covered by expansion, and how the expansion group compares to the state’s total Medicaid population in that age range. Once in a state profile, use the drop-down box to select county, state senate district, or state house district for data breakdowns. Click the U.S. map outline, in the upper right corner, to return to the national map.
States ending or reducing expansion coverage would have an outsized impact on older adults, affecting more than half of all the 50–64-year-olds enrolled in the program statewide. Millions of older Medicaid enrollees in counties and state legislative districts around the country will feel the impact of an expansion rollback.
Medicaid Expansion Analysis Methodology
State
Avalere Health estimated the adult Medicaid expansion enrollment numbers from the latest Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) enrollment reports (November 2024) and projected 2025 enrollment utilizing Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projections. To break out the expansion population into the age groups of interest, Avalere Health applied data extracted from American Community Survey and the Small Area Health Insurance Estimates (SAHIE) Interactive Data Tool via the US Census Bureau website.
County
Using the SAHIE data, Avalere Health estimated the county-level expansion population by leveraging the proportion of insured people below 138 percent of Federal Poverty Level per county and the previously calculated state expansion numbers.
House and Senate Districts
Avalere Health utilized the State Legislative District files from the Census website to crosswalk county populations to House and Senate district populations, respectively.
Rounding
State numbers are rounded to the 1,000th place, while county and legislative district numbers are rounded to the 10th place. All counts below 11 are suppressed. Totals for the same population may differ across tabs due to rounding.